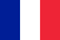
In addition to onychomycosis, there are many other causes and diseases that can change the normal appearance of nails. Thick, cloudy white nails can be the result of psoriasis or unsuccessful use of harsh cosmetics. Separation and stratification of the nail plate occurs in both injuries and trophic disorders of the lower extremities with varicose veins or endocrine diseases. Onychomycosis very often begins not with changes on the nail plate itself, but with redness, itching and peeling of the skin surrounding the nail. If a person does not pay attention to these symptoms, the fungus begins to develop, penetrating deeper tissues, incl. under the nails. The fungus on the nail plate usually starts from its free edge, which thickens, becomes gray-yellow, easily breaks and crumbles. But even in this case, it is possible to precisely determine the presence of fungi only with the help of laboratory research - microscopy.
Thick, cloudy white nails can be the result of psoriasis or unsuccessful use of harsh cosmetics. Separation and stratification of the nail plate occurs in both injuries and trophic disorders of the lower extremities with varicose veins or endocrine diseases. Onychomycosis very often begins not with changes on the nail plate itself, but with redness, itching and peeling of the skin surrounding the nail. If a person does not pay attention to these symptoms, the fungus begins to develop, penetrating deeper tissues, incl. under the nails. The fungus on the nail plate usually starts from its free edge, which thickens, becomes gray-yellow, easily breaks and crumbles. But even in this case, it is possible to precisely determine the presence of fungi only with the help of laboratory research - microscopy.
The fungus occurs only in the elderly and chronically ill.
In patients with chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, peripheral vascular diseases, etc. ) nail fungus is indeed more common, but only because all these diseases reduce the activity of general and local immunity, negatively affect the skin's resistance to any infections. Age, by itself, cannot be the cause of fungal diseases, but the older a person gets, the more health problems accumulate that contribute to the development of fungal infections. At the same time, completely healthy young people are not protected from onychomycosis. Sports fans can suffer from nail fungus. blisters, microtraumas of the skin of the feet and sweating create ideal conditions for the development of fungi. The fungus can occur in those who have to spend most days on their feet, in closed shoes that do not allow excess moisture to evaporate. Smoking, frequent stress and excessive love of sweets increase the risk of developing fungal infections.
The fungus is usually infected in the pool, sauna or on the beach.
In a sauna, swimming pool or on the beach, the risk of encountering the fungus is really very high, as in any other place with high temperature and humidity, where the spores of the cause of onychomycosis remain long-lasting. But this is not far from the only opportunity for onychomycosis infection. The causes of fungal infections can get on the skin of a person who visits a gym, beauty salon, shoe store, public transportation or simply wears someone else’s slippers. But contact with the fungus or its spores does not always lead to the development of infection, much depends on the condition of the skin and the body as a whole. And only if the fungus enters the optimal environment for development and finds a weak place in the immune defense of the human body, it can cause damage to the skin and nails. Risk factors for the development of onychomycosis are considered to be dry blisters and cracks on the skin of the feet, increased sweating of the feet, wearing tight shoes and "non-breathable" shoes, as well as synthetic socks.
Fungal spores are everywhere, there is no effective protection against them.
Fungal spores can indeed be found almost everywhere, even at home, so it is impossible to completely rule out contact with them. Yet, even a person at high risk of developing mycosis has the opportunity to protect themselves from developing this infection. First of all, you must carefully follow the rules of personal hygiene: use only your own shoes, towels, etc. It is equally important to carefully monitor the condition of the skin of the feet and nails - remove dry blisters in time, properly treat cracks, scratches and nails. It will not be superfluous to prevent excessive sweating of the feet, including the use of antiperspirant foot products. If the risk of onychomycosis is very high, then you can prophylactically (once a week) cover the nails with a special antifungal varnish. Also, after consulting your doctor, you can start taking drugs that increase immunity - interferon inducers, drugs based on plant adaptogens, multivitamin complexes.
Mushrooms are forever. You can’t get rid of it completely.
Onychomycosis is a common infectious disease that ends as soon as its pathogen is removed from the body. This can only be prevented by wrong treatment or the mistakes of the patient himself. The peculiarity of onychomycosis is that the fungus is located under the nail plate (in the nail bed). Not every LP can penetrate that deep. Therefore, today for the treatment of onychomycosis the use of special forms of external means or systemic antifungal therapy is recommended. Moreover, treatment must be continued even if all symptoms of the fungal infection have disappeared. You can stop taking the medicine only after 3 repeated examinations (microscopy) show that the fungus is no longer in the tissues. In addition, the use of antifungal agents must be combined with proper nail and foot care. this reduces the risk of new relapses.
It is useless to treat fungi with external means.
Modern forms of external preparations enable the creation of a high concentration of antifungal agent in the affected area. At the same time, external agents are not absorbed into the systemic circulation, have a wider spectrum of action and a low risk of developing resistance. Unfortunately, not all external drugs are able to penetrate the thickness of the nail, especially into the nail layer tissue, where the majority of pathogens are located. Therefore, local therapy is recommended to be combined with the removal of the nail plate or the use of keratolytic agents - urea or salicylic acid preparations. This is especially important if onychomycosis is accompanied by hyperkeratosis of the nail. Usually, monotherapy with external means is used in cases when the nails of 1-2 fingers or 1/3 of the surface of the nail plates are affected. In other cases, external agents are used in combination with systemic antifungal drugs.
Antifungal tablets are very dangerous and toxic.
Due to the long duration of antifungal treatment (in some cases up to 12 months) there is indeed a risk of side effects and toxic effects on the liver. But today, methods have been developed that allow you to minimize this danger. Thus, for example, some antifungal drugs are used in the regime of pulse therapy: ie. short, 5-7-10-day courses, with a break of 21 days. There are systemic antifungals that can only be taken 1-2 times a week. There are high safety profile antifungals that, when taken in therapeutic doses, do not have a negative effect on liver cells even with long-term continuous use. Therefore, it is most important not to take systemic antifungal agents without a doctor’s appointment and supervision. Only a dermatologist should prescribe such funds.
If you choose the right medicine, the fungus can be cured in a week.
It is possible to stop the development of a fungal infection in a short time only if the infection occurred recently and the cause of onychomycosis did not have time to penetrate deep into the tissues surrounding the nail. But, unfortunately, few patients seek medical help at this stage, most often the treatment of onychomycosis begins in the later stages, when the nail plate (or even several) is seriously affected and the process of dystrophy or hyperkeratosis actively lasts in the surrounding tissues. In such a situation, no medication will help to quickly solve the fungal problem, even if the treatment is combined with complete removal of the affected nail plate, it will take about 3 months to restore the nail. In a relatively short time, approximately 4-6 weeks, you can reduce only the most noticeable symptoms of onychomycosis. But the cause of the infection, especially in the form of spores, still remains in the tissues. And only after completing the course of treatment prescribed by a doctor, you can get rid of this unpleasant disease.